77) What Is Meant By Deadlock In DBMS?
Answer: A deadlocks involves a chain of transactions that are cyclically waiting for each other to release a lock. The DBMS detects deadlock with a transaction dependency graph. It resolves the impasse by sacrificing one of the transactions in cycle.
78) What Are The Three Techniques For Handling Deadlocks?
Answer: Three techniques used for handling deadlocks are:
- Timeouts
- Wait for only a system-defined period of time.
- Deadlock Prevention
- Order transactions using transaction timestamps.
- Wait-Die
- Wound-Wait
- Deadlock Detection
- Wait-For Graph
79) How You Can Identify, Prevent & Resolve A Deadlock?
Answer: Detecting and resolving deadlocks as they arise has advantage over taking measures to prevent deadlock, because deadlocks tend to be rare. The lock manager maintains a Waits-For Graph to detect deadlock cycles.
DBMS allows deadlock to occur but recognizes occurrences of deadlock and break them. Deadlock can be prevented by giving each transaction a priority (e.g., assign Timestamp) and ensuring that lower priority transactions are not allowed to wait for higher priority transactions (or vice-versa).
80) What Is Timestamping? Between Timestamping & Locking Which Is A Better Concurrency Control Technique?
Answer: Timestamping is a concurrency control protocol that orders transactions in such a way that older transactions get priority in the event of conflict.
- Generally, timestamping is superior in situations where either most transactions are read-only, or it is rare that concurrent transactions will try to read and write the same element.
- In high-conflict situations, locking performs better.
- Locking will frequently delay transactions as they wait for locks, and can even lead to deadlocks where several transactions for a long time, and then one has to be rolled back. But if concurrent transactions frequently read and write elements in common, then rollbacks will be frequently, introducing even more delay than a locking system.
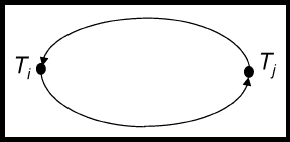
81) What Is A Wait For Graph?
Answer: A Wait-for Graph (WFG) is a useful tool to identify deadlocks. Basically it's a graphical notation to represent wait for relations among transactions.
- The nodes represent transactions
- An edge from Ti to Tj indicates that Ti is waiting for Tj
- If the WFG has a cycle, then there is a deadlock situation.
ALSO CHECK THE BELOW FAQ's:
66) What is Fourth (4th) Normal Form (4NF)?
67) What is Fifth (5th) Normal Form (5NF)?
68) What Are The Lossless Inference Rules For Functional Dependencies (FD's) Or State The Armstrong's Axioms?
69) What Is Domain-Key Normal Form (DKNF)?
70) Define Transaction? Explain Different States Of Transaction?
71) Describe The ACID Properties Of A Transaction?
72) What Is Schedule & What Is The Importance Of Schedule?
73) What Do You Mean By Serializability In Transaction Processing?
74) What Are The Two Methods That Guarantee Serializability?
75) What Is Locking? What Are The Types Of Locking?
... Return To DBMS FAQ's Main Page.
... Return To HR Interview Questions With Answers Main Page.
Thank you
ReplyDeleteIts so helpful
Santosh